Fri 30 January 2026
Security testing relies on a rule-based approach or on a form of intelligence fuzzing that executes checks without adapting to the systems they tested.
These tools follow fixed logic and repeat the same tests across environments. As we are entering a new era of Autonomous AI Security Agents, which can showcase understanding of system behavior, adapt their testing strategies in real time, and explore applications dynamically, enabling more contextual and intelligent security testing.
In professional pentesting today, the primary challenge is no longer identifying isolated bugs, but the chaining and post-exploitation of multi-stage vulnerabilities.
This list provides a comparative analysis of the core functionalities of eight open-source AI penetration testing tools.
List Of Open Source AI pentest tools
Github Metrics Comparison
| Tool | Stars | Commits | Contri-butors | Last Commit | License | Tech Stack |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PentestGPT | 11k+ | 300+ | 22+ | ~3 weeks ago | MIT | Python (77%), HTML (19%) |
| Pentagi | 900+ | 188+ | 8+ | ~1 week ago | MIT | Go (79%), TypeScript (20%) |
| HexStrike AI | 5.9k+ | 60+ | 2+ | ~4 months ago | MIT | Python |
| Strix | 19k+ | 205+ | 19+ | < 24 hours ago | Apache-2.0 | Python (66%), Jinja2 (30%) |
| CAI | 6.7k+ | 1065+ | 93+ | Last month | MIT | Python (98.6%) |
| Nebula | 843+ | 501+ | 4+ | Last month | BSD-2- Clause | Python (93%) |
| Neurosploit | 614+ | 29+ | 3+ | ~3 months ago | MIT | Python (85%), C++ (14.9%) |
| Deadend CLI | 100+ | 206+ | 2 | < 24 hours ago | AGPL-3.0 | Python (78.5%) JavaScript (4.1%) Jinja (3.1%) Rust (3.1%) CSS (3.0%) HTML (2.2%) |
1. PentestGPT
PentestGPT is an open-source framework designed to automate parts of the penetration testing process using Large Language Models (LLMs).
The tool uses three interacting modules to automate attack chains while keeping track of the overall testing progress:
Reasoning Module: Acts as the lead strategist. It maintains a "task tree" to manage the big picture and decide the next logical step in the attack.
Generation Module: Functions as the executor. It takes the strategy from the reasoning module and creates the specific terminal commands or scripts needed to perform the task.
Parsing Module: Acts as the data analyst. It cleans up the raw, messy output from security tools, extracting only the most important findings to feed back into the system.
By using this three-part system, PentestGPT can handle complex, multi-stage attacks without losing track of previous results or getting stuck in repetitive loops.
Key Features:
The features of PentestGPT are built to automate the most difficult parts of a penetration test:
Automated Reasoning Engine: The platform utilizes large language model logic to solve complex penetration testing tasks and Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges.
Dynamic Session Tracking: The system provides a live walkthrough that records and displays every step of the testing process in real-time.
Cross-Domain Security Support: It covers multiple specialized categories, including web security, cryptography, reverse engineering, forensics, and binary exploitation (PWN).
Live Activity Monitoring: Users can observe the agent’s reasoning and progress through a continuous real-time feedback loop.
Modular Framework Design: The extensible architecture allows for the integration of new security tools and customized testing modules.
PentestGPT suffers from limited and unclear documentation. During setup, we attempted to run it via OpenRouter using a specific provider (MoonshotAI), but the tool consistently defaulted to the OpenAI provider. After manually forcing the provider change to MoonshotAI, the tool stalled during initialization and remained unresponsive for an extended period, preventing effective testing.
2. PentAGI
PentAGI is an open-source, autonomous system that coordinates multiple AI agents to perform complex security tests. It uses a "multi-agent" approach, where specialized AI roles such as research, coding, and infrastructure work together to independently discover, analyze, and exploit vulnerabilities. The tool executes all tasks in a secure, isolated Docker environment, using its own browser and search systems to gather real-time intelligence and adapt its attack strategy without human intervention.
Key Features:
These are the main features that PentAGI provides :
Fully Autonomous Agent: An AI-powered system that automatically determines and executes the next steps in a penetration test without human help.
Secure Sandboxing: All operations run inside an isolated Docker environment to keep the host system safe and prevent any accidental damage.
Built-in Security Suite: Includes over 20 professional tools (like Nmap, Metasploit, and Sqlmap) that the AI can run and interpret on its own.
Smart Memory & Search: Uses a long-term memory system to store research and integrates with web search engines to find the latest CVE data.
Specialist Team: Uses a "delegation" system where different AI agents focus on specific tasks like research, coding, or infrastructure.
Modern Web Dashboard: Features a clean interface and detailed logging so you can monitor the AI’s progress and findings in real-time.
Pentagi has a long and complex setup with limited documentation and unclear instructions, making it difficult to run the tool against vulnbank.org.
3. HexStrike AI
HexStrike AI is an MCP server that connects LLMs to 150+ security tools. It lets AI agents run their own penetration tests, find vulnerabilities, and automate bug bounty tasks without manual input. Essentially, it gives models like Claude and GPT a "hands-on" toolkit to perform offensive security work.
Key Features:
HexStrike AI MCP uses a multi-agent architecture to handle autonomous testing and vulnerability data.
Agent Connection: Models like Claude and GPT connect through the FastMCP protocol to execute commands.
Target Analysis: The decision engine evaluates targets to select specific testing strategies and tools.
Autonomous Execution: Agents perform security assessments across environments without manual intervention.
System Adaptation: The platform updates its testing logic in real-time based on results and found vulnerabilities.
Technical Reporting: The system generates vulnerability cards and risk analysis data for the final output.
HexStrike AI operates as an MCP (Model Context Protocol) server rather than a standalone testing engine.
4. Strix
Strix is an autonomous agent framework designed to simulate human attacker behavior by executing code in dynamic environments. It identifies security flaws and confirms their validity by generating functional proof-of-concept exploits. This approach provides developers and security teams with verified results, reducing the manual effort required for penetration testing and the noise typically associated with static scanning.
Key features:
Automated Application Security: Strix utilizes an integrated hacker toolkit to dynamically detect and validate critical vulnerabilities in your code. By running applications in real-time, it finds runtime flaws that static tools miss and confirms them with proof-of-concept evidence.
Rapid On-Demand Pentesting: By deploying teams of collaborating agents, the system scales across entire infrastructures to complete penetration tests in hours instead of weeks. This autonomous scale allows organizations to generate compliance-ready reports and risk analysis on demand.
Bug Bounty Research & Validation: The platform automates the end-to-end bug hunting process, from initial discovery to exploit generation. It removes the manual overhead of research by autonomously finding bugs and creating the functional PoCs required for faster reporting and rewards.
DevSecOps & CI/CD Integration: A developer-first CLI allows for seamless embedding into CI/CD pipelines. This enables the system to autonomously block vulnerabilities before they reach production, providing auto-fix suggestions and actionable reports directly to the engineering team.
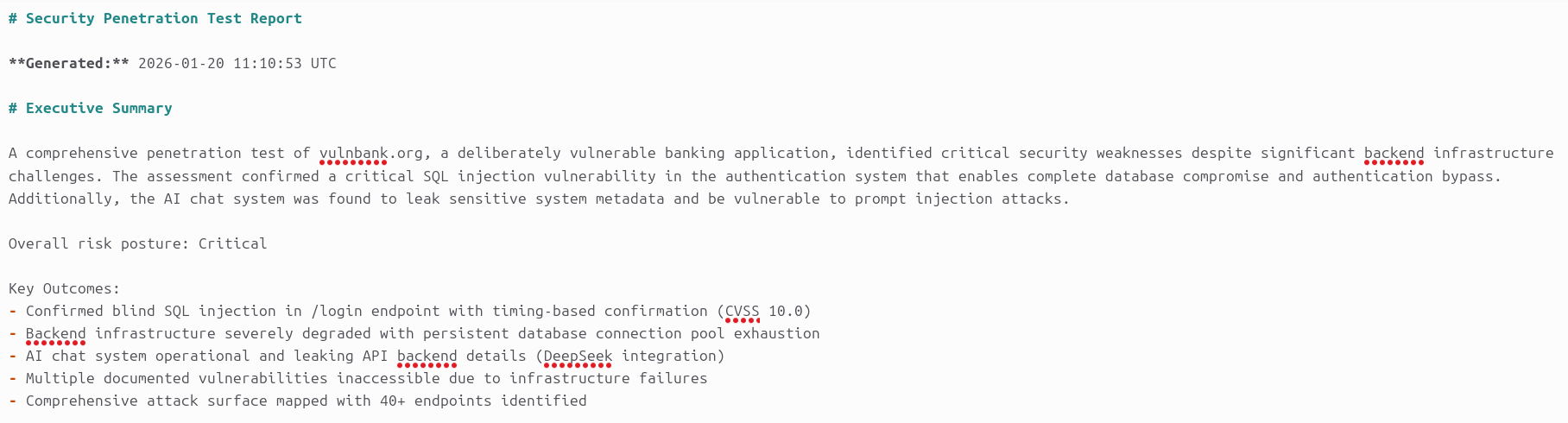
We ran the Strix framework against vulnbank.org and identified multiple critical vulnerabilities, including:
- Confirmed blind SQL injection in /login endpoint with timing-based confirmation. (CVSS 10.0)
- Backend infrastructure severely degraded with persistent database connection pool exhaustion.
- AI chat system operational and leaking API backend details. (DeepSeek integration)
- Multiple documented vulnerabilities inaccessible due to infrastructure failures.
- Comprehensive attack surface mapped with 40+ endpoints identified.
5. Cybersecurity AI (CAI)
CAI is an open-source framework for building and deploying AI agents for offensive and defensive security tasks. It provides a modular environment for developers and researchers to automate vulnerability discovery, exploitation, and mitigation. Used across various organizations, the framework serves as a standardized infrastructure for creating specialized security agents.
Key Features:
The CAI framework provides a modular set of features designed to bridge the gap between AI models and practical security operations.
Broad Model Integration: CAI provides native support for over 300 models, including OpenAI, Anthropic, DeepSeek, and local deployments through Ollama.
Integrated Offensive Toolset: The framework includes pre-configured tools for reconnaissance, vulnerability exploitation, and privilege escalation(gaining unauthorized admin-level control) to streamline security workflows.
Validated Performance: The architecture is verified through practical applications in CTF environments, bug bounty programs, and professional security assessments.
Modular Agent Architecture: The system uses a task-specific framework that allows users to build and deploy specialized agents tailored to distinct security objectives.
Execution Guardrails: Built-in security protocols protect the environment against prompt injection and the execution of unauthorized or dangerous commands.
Community Research Focus: Designed as a research-first platform, the framework aims to standardize and open-access AI-driven cybersecurity tools for the broader community.

We ran the CAI framework against vulnbank.org and identified multiple high- and critical-severity vulnerabilities, including:
-
SQL injection allowing authentication bypass and full account takeover
-
Exposed Werkzeug debugger enabling potential remote code execution
-
Insecure direct object references allowing cross-account data access
-
Unrestricted money transfer functionality enabling unauthorized fund transfers
-
Unlimited account registration allowing fraud and abuse at scale
-
Verbose error messages disclosing internal application logic
-
JWT token injection issues leading to session and privilege abuse
6. Nebula
Nebula is an open-source penetration testing assistant that integrates large language models directly into the command-line interface. It automates technical tasks such as reconnaissance, vulnerability analysis, and session documentation. By interpreting terminal outputs in real-time, the tool provides suggestions for further testing and maintains an automated log of findings and command history.
Key Features:
Nebula offers a comprehensive suite of AI-enhanced features to automate the data-gathering and documentation phases of a security engagement.
Agentic Internet Search: The tool uses AI agents to pull real-time cybersecurity context and news from the web, ensuring users are informed about the latest trends, such as the emerging VoidLink cloud malware or the recently disclosed Gogs RCE zero-day.
Automated Note-Taking: Nebula handles the recording and categorization of technical findings, mapping them to security standards like CWE and NIST without manual intervention.
Context-Aware Insights: The system analyzes live terminal outputs from security tools and provides immediate suggestions for next steps, such as specific vulnerability discovery or exploitation techniques.
Multi-Source Tool Integration: Users can import data from external reconnaissance and scanning utilities to centralize analysis and generate AI-driven remediation advice.
Integrated Evidence Capture: The platform includes tools to snap screenshots and add quick notes or highlights directly from your command screen. This makes it much faster to gather the proof you need for your final report
Action Logging: The system maintains a comprehensive audit trail by automatically logging every command executed alongside manual technical notes for a complete session history.
Live Activity Feed: A real-time status panel monitors ongoing activities and engagement progress, refreshing every five minutes to keep testing phases on track.
Nebula is an interactive AI terminal assistant, not an autonomous penetration testing tool, and therefore cannot be executed fully autonomously against a target. It is used to aid with human-driven testing by assisting with commands, payloads, and analysis rather than producing standalone findings.
7. NeuroSploit
NeuroSploit is an AI-driven penetration testing ecosystem built to automate and enhance multiple facets of offensive security tasks. By utilizing the power of large language models (LLMs), the framework offers dedicated agent personas capable of target analysis, vulnerability detection, exploitation planning, and defensive support, maintained through a focus on operational security and ethical standards.
Key Features:
NeuroSploit is a smart "assistant" for hacking. It uses an AI "brain" (LLM) to help security experts automate the boring parts of their work. Instead of just running one scan at a time, it uses specialized AI agents to plan attacks, find weak spots, and test defenses much faster than a human could manually.
Specialized Agent Ecosystem: The framework uses a role-based system to deploy agents tailored for specific operations, such as Red Teaming for attack simulation, Blue Teaming for defensive audits, or Malware Analysis for threat inspection.
Multi-Model & Local Execution: It integrates with a wide array of LLM providers including Gemini, Claude, and GPT, and offers native support for LM Studio and Ollama to allow for completely local, private execution.
Automated Tool Orchestration: The system can chain together external security tools like Nmap, Metasploit, and Nuclei, allowing AI agents to autonomously manage complex reconnaissance and exploitation workflows.
Vulnerability Validation & Intelligence: Beyond simple scanning, the platform includes built-in OSINT collectors and DNS enumerators to gather target intelligence and perform lateral movement and persistence testing.
High-Fidelity Reporting & Guardrails: To ensure professional results, the framework generates structured HTML and JSON reports while using grounding and self-reflection techniques to minimize AI hallucinations and false positives.
NeuroSploit was unable to start properly due to issues during initialization, which prevented it from running tests or producing meaningful results.
8. Deadend CLI
Deadend CLI is an autonomous agent for penetration testing that uses self-correction to overcome security blocks. When a traditional attack fails, the agent reads the error response to understand the specific defense in place, then writes custom Python code to bypass it. This continuous cycle of acting and learning allows the tool to evolve its tactics in real-time until it successfully breaches the target.
Key Features:
Deadend CLI utilizes a specific set of architectural features to enable local, autonomous web penetration testing.
Local Execution: The system runs entirely on local infrastructure with no cloud dependencies, ensuring zero data exfiltration during security assessments.
Flexible LLM Support: The framework is designed to be compatible with any deployable large language model rather than being locked to a specific provider.
Sandboxed Tool Integration: It utilizes custom sandboxed environments, including Playwright, Docker, and WebAssembly, to execute testing tools securely.
Supervisor and Sub-agent Design: The system uses a simple hierarchy where a "Supervisor" AI manages the big picture and assigns specific jobs to "Sub-agents”. This keeps complex tasks organized and ensures the right AI is doing the right job at the right time.
Smart Decision-Making: Instead of just guessing, the AI uses a "Confidence Filter." Before it takes an action, it checks how sure it is of success. Depending on the score, it decides whether to move forward (Green), try a different approach (Yellow), or stop to double-check its facts (Red).
Despite configuring Deadend CLI to use Gemini, the tool continued to default to the OpenAI provider. Since OpenAI was not configured, execution failed, preventing effective use of the tool against test targets.
Conclusion
We tested eight open-source AI pentesting tools against a banking web application(vulnbank.org) to evaluate their effectiveness.
Strix and Cybersecurity AI (CAI) delivered actionable results, confirming critical vulnerabilities and producing proof-of-concept exploits, including SQL injection, authentication bypass, and insecure object references.
PentestGPT, PentAGI, NeuroSploit, and Deadend CLI encountered setup or execution issues that prevented them from completing tests effectively, such as initialization failures, database errors, or LLM provider misconfigurations.
HexStrike AI functions as an MCP server, requiring a compatible AI client to orchestrate tests, while Nebula operates as an AI-assisted terminal tool that supports human-driven testing with guidance and next-step suggestions but does not run autonomously.
Overall, Strix and CAI stand out as the most reliable options for professional security teams, while the other tools remain useful for research, experimentation, or assisted workflows depending on the environment and setup.